Connect Methods
Overview
A connect method is the software used to connect to a reserved node.
Before 2.3, there were only a few, fixed connect methods used - RDP for Windows and ssh for Linux. In 2.3, the first stage of configurable connect methods was introduced. Potentially any connect method can now be configured for an image. For stage one, VCL admins must manually add available connect methods to the VCL database. Stage two will provide a way for available connect methods to be managed through the VCL web site.
There are two types of connect methods: those that can be automatically provisioned by vcld (or are considered to be part of an OS by default) and those that must be manually installed in the image by the image maintainer. Either type can be added to VCL and mapped to an image.
Connect Method schema
Understanding the connect method database schema is key to managing the available connect methods. There are two tables:
- connectmethod - defines what connect methods exist
- connectmethodmap - defines how connect methods can be mapped and maps them to images
connectmethod definition:
-
id - id of connect method
-
name - name of connect method
-
description - description of connect method - displayed on edit image page
-
protocol - TCP/UDP - type of protocol (for firewall rules)
-
port - port connect method will be listening on (for firewall rules and Connect page)
-
connecttext - text to be displayed on the Connect page - some special keys for string substitution can be used in this
-
servicename - Windows service name or Linux process name that can be found when the service is running
-
startupscript - script that can be run to start the service
-
**description_<locale>** - description in a different language; replace <locale> with the desired locale (ex: description_ja_JP)
-
**connecttext_<locale>** - connecttext in a different language; replace <locale> with the desired locale (ex: connecttext_ja_JP)
keys for connecttext string substitution:
- #userid# - replaced with user.unityid for the current user
- #password# - replaced with reservation.pw for the selected reservation
- #connectIP# - replaced with computer.IPaddress for the currently reserved node
- #connectport# - replaced with reservation.connectport if populated or connectmethod.port for this connect method if not
connectmethodmap definition:
- connectmethodid - reference to connectmethod.id
- OStypeid - reference to OStype.id (can be NULL)
- OSid - reference to OS.id (can be NULL)
- imagerevisionid - reference to imagerevision.id (can be NULL)
- disabled - 0/1
- autoprovisioned - 0/1/NULL
This table is “overloaded”, meaning it is used for two things. It both describes which connect methods can be mapped to an image/OS/OStype (entries with autoprovisioned set to 0 or 1) and which connect methods are mapped to an image/OS/OStype or not (entries with autoprovisioned set to NULL).
Only one of OStypeid, OSid, or imagerevisionid can have a non-NULL value. (i.e. A mapping is only done to an OS type or an OS or an image revision.)
The disabled field allows exceptions to be made. For example, if RDP is mapped to the Windows OS type, but there was an image where VNC should be used instead, entries would be added for any imagerevisionid of that image for RDP with disabled set to 1.
Default entries
The schema provided with Apache VCL 2.3 has four connect methods by default:
- ssh
- RDP
- iRAPP RDP
The default mapping for these methods is as follows:
- ssh can be autoprovisioned to linux
- ssh can be autoprovisioned to unix
- RDP can be autoprovisioned to windows
- iRAPP RDP can be autoprovisioned to osx
- ssh is mapped to linux
- ssh is mapped to unix
- RDP is mapped to windows
- iRAPP RDP is mapped to osx
Here are two of the actual table entries in connectmethodmap (values from referenced tables are in ()‘s):
| connectmethodid | OStypeid | OSid | imagerevisionid | disabled | autoprovisioned |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (ssh) | 2 (linux) | NULL | NULL | 0 | 1 |
| 2 (RDP) | 1 (windows) | NULL | NULL | 0 | 1 |
| 1 (ssh) | 2 (linux) | NULL | NULL | 0 | NULL |
| 2 (RDP) | 1 (windows) | NULL | NULL | 0 | NULL |
The first two entries listed above mean that those connect methods can be selected for being autoprovisioned for the specified OS. Specifically, the first entry means that on the edit image profile page for any linux images, ssh will be available as a connect method that can be selected for that image. The second entry means that on the edit image profile page for any windows images, RDP will be available as a connect method that can be selected for that image.
The second two entries mean that those connect methods are enabled for the specified OS. Specifically, the third entry means that on the edit image profile page for any linux images, ssh will be selected as one of the enabled connect methods. The fourth entry means that on the edit image profile page for any windows images, RDP will be selected as one of the enabled connect methods.
Examples
Adding VNC as an available option for Linux
In this example, we add VNC as an available connect method that can be selected on edit image profile page for any Linux images. However, we’ll set it with autoprovisioned set to 0, meaning that the image maintainer is responsible for installing VNC in the image.
First, we need to add VNC to the connectmethod table:
| id | name | description | protocol | port | connecttext | servicename | startupscript |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | VNC | VNC on port 5900 | TCP | 5900 | (listed below) | Xvnc | /etc/init.d/vncserver start |
This could be used as the connecttext:
You will need to have a VNC client on your local computer to connect to the system.
Open your VNC client and use the following information when you are ready to connect:<br>
<UL><br>
<LI><b>Remote Computer</b>: #connectIP#</LI><br>
<LI><b>Remote Port</b>: #connectport#</LI>;<br>
<LI><b>User ID</b>: #userid#</LI><br>
<LI><b>Password</b>: #password#</LI><br>
</UL>
Next, we create an entry in the connectmethodmap table that allows VNC to be selected for any Linux images, but not as an autoprovisioned method (note that this only allows it to be selected, it does not actually assign it to be selected for anything):
| connectmethodid | OStypeid | OSid | imagerevisionid | disabled | autoprovisioned |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 2 | NULL | NULL | 0 | 0 |
Now, under the subimages section of the edit image profile page for any Linux images, “VNC on port 5900” will be available as a connect method that can be assigned. If it is selected, a warning message will be displayed stating that VCL cannot autoprovision VNC and that it must have already been installed in the image by the image maintainer.
Adding xRDP for Linux and Enabling it for OS type Fedora 16
In this example, we’ll add xRDP as an available option for any Linux images and set it as enabled for the OS type Fedora 16. We’ll use 23 as OS.id for Fedora 16.
First, we need to add xRDP to the connectmethod table:
| id | name | description | protocol | port | connecttext | servicename | startupscript |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | xRDP | xRDP | TCP | 3389 | (listed below) | xrdp | /etc/init.d/xrdp start |
This could be used as the connecttext:
You will need to have an RDP client to connect to the system.
Open your RDP client and use the following information when you are ready to connect:<br>
<UL><br>
<LI><b>Remote Computer</b>: #connectIP#</LI><br>
<LI><b>User ID</b>: #userid#</LI><br>
<LI><b>Password</b>: #password#</LI><br>
</UL>
Next, we create an entry in the connectmethodmap table that allows xRDP to be selected for any Linux images, and another entry that enables it for all Fedora 16 images.
| connectmethodid | OStypeid | OSid | imagerevisionid | disabled | autoprovisioned |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 2 | NULL | NULL | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | NULL | 23 | NULL | 0 | NULL |
Now, under the subimages section of the edit image profile page for any Linux images, “xRDP” will be available as a connect method that can be assigned. If it is selected, a warning message will be displayed stating that VCL cannot autoprovision xRDP and that it must have already been installed in the image by the image maintainer. Additionally, for any Fedora 16 images, it will be listed as an assigned connect method by default (note: Fedora 16 does not include xRDP by default, it’s just being used an example here).
Understanding entries created by removing a default entry from an image
This is not something that a VCL admin would need to do manually in the database, but it is useful to understand what happens in the database when a connect method that is mapped by OS type or OS is removed from an image revision. Building on the xRDP example above, we start with the following entries in the connectmethodmap table, remember that connectmethod.id 5 is xRDP, OStype.id 2 is Linux, and OS.id 23 is Fedora 16:
| connectmethodid | OStypeid | OSid | imagerevisionid | disabled | autoprovisioned |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 2 | NULL | NULL | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | NULL | 23 | NULL | 0 | NULL |
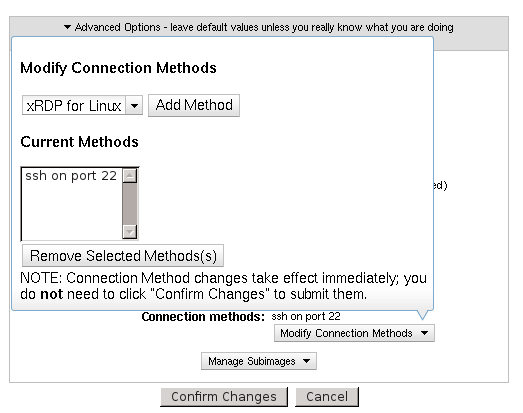
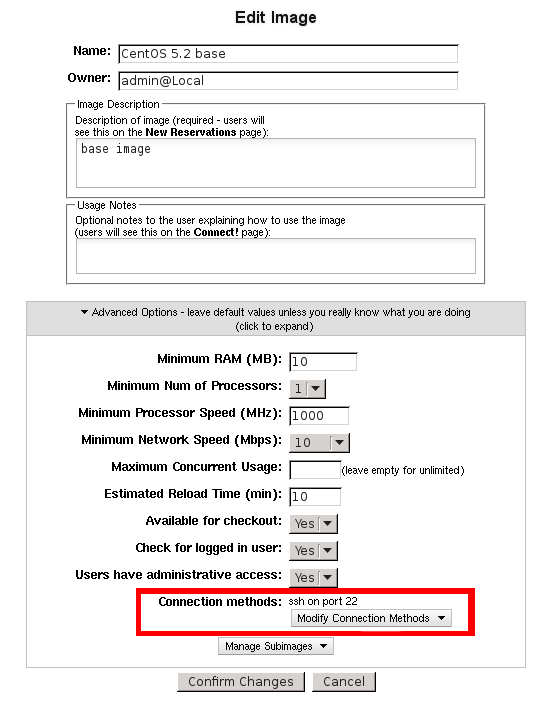
Let’s say we’ve created a web server image based on Fedora 16 from which we’ve removed X11, meaning that xRDP will no longer work as a connect method for this image. Instead, we just want to have ssh as the only connect method available for this image. We’d go to Manage Images->Edit Image Profiles->Edit for that image. Then, we’d expand the Advanced Options section, and click on Modify Connection Methods. Next, if ssh is not already enabled as a connect method, we’d select it from the drop-down box and click Add Method. Finally, we’d select xRDP from the list of enabled connect methods, and click Remove Selected Method(s). This final step of removing xRDP would add the following entry to the connectmethodmap table (we’ll use 582 as the imagerevisionid of the web server image):
| connectmethodid | OStypeid | OSid | imagerevisionid | disabled | autoprovisioned |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | NULL | NULL | 582 | 1 | NULL |
The above entry means, “disable connect method 5 (xRDP) for image revision 582 (web server) even if it is enabled for the image’s OS or OS type”.
Screen Shots
Here are some screen shots to know what things look like in the web interface.
This image has the Connect Methods section of the Edit Image Profile page highlighted.
This image has the Connect Methods dialog open.